Cultivation Guide
INTRODUCTION
The strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus Fragaria, collectively known as the strawberries. It is cultivated worldwide for its fruit. The fruit is widely appreciated for its characteristic aroma, bright red color, juicy texture, and sweetness. It is consumed in large quantities, either fresh or in such prepared foods as preserves, juice, ice creams, milkshakes, and chocolates. Artificial strawberry flavorings and aromas are also widely used in many products like lip gloss, candy, jam, jelly and many others.
In India Mahabaleshwar is famous Hill Station and Famous for strawberries where 80% of strawberries are being cultivated, strawberries are also cultivated in other regions of India like Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Kolkata, Hyderabad, Ooty, J&K, Rajasthan etc.
Strawberries are rich source of antioxidants they support the immune system they may help with blood sugar regulation they may have antimicrobial effects they may improve heart health they can help with weight management Strawberries are also been credited as having cancer- fighting compounds.
Nutritional and health values of the strawberry fruit
Energy |
45 cal |
Vitamin A |
45 IU |
Protein |
1.0 g |
Vitamin C |
94 mg |
Fat |
0.0 g |
Niacin (Vitamin B3) |
540 mcg |
Carbohydrate |
11 g |
Folate |
29.38 mcg |
Dietary fiber |
2.0 g |
Manganese |
540 mcg |
Calcium |
23.2 mg |
Iron |
0.6 mg |
Magnesium |
16.6 mg |
Selenium |
1.16 mg |
Potassium |
170 mg |
Zinc |
0.2 mg |
Phosphorous |
31.5 mg |
Sodium |
0 mg |
SOIL REQUIREMENT
Strawberries are perennials that need rich soil with lots of organic matter and a slightly acidic pH (between 5.5 and 6.5). Work in compost, rotted manure and some peat moss at planting time. Another good addition is granular fertilizer. Strawberries can adapt very well to wide range of soils strawberries can perform excellent in well-drained sandy loam soils at least 12inches deep heavy soil provide good result if drained is adequate
Some strawberry varieties which easily come in contact with fungal diseases in the soil for many years because of the crops which were cultivated before in the same filed, we highly suggest you to plant strawberries in a newly prepared filed where you have not planted potatoes, tomatoes, eggplant, raspberry, blueberry, blackberry, gooseberry, cherries.
CLIMATE
Strawberry can be classified according to the suitability of varieties for a specific period there are three types of strawberries being grown commercially Short Day, Day Neutral, and ever bearing
SELECTION OF VARIETIES:
Short day or "June Bearing" strawberries produce a single, large crop per year during a 2 – 3 week period in the spring. June bearers are the traditionally grown plants, producing a single flush of flowers and many runners. They are classified into early, mid-season and late varieties like
Ever bearing strawberry plants also produce fewer runners. The fruit of ever bearing strawberries is generally smaller than June-bearing strawberries too
Day neutral strawberry plants are unique. Unlike June bearing varieties, day neutral strawberries will produce a good yield in the first year they are planted. They flower and set strawberries whenever the temperature is between 35 and 85 degrees
Strawberry is an important fruit crop of India and its commercial production is possible in temperate and sub-tropical areas of the country. Varieties are available which can be cultivated in the subtropical climate. In India, it is generally cultivated in the hilly areas.
Varieties:
AMIGA |
MARGHERITA |
WINTER DAWN |
SELVA |
CAMAROSA |
MARISOL |
WINTER STAR |
SHAKED |
FESTIVAL |
ROCIERA |
FLAVIA |
PELES |
NABILA |
SA |
FLAMINIA |
ROTEMI |
KEMILA |
SWEET CHARLIE |
RANIA |
VENTENA |
MELLISA |
SWEET SENSATION |
FORTUNA |
VERTONA |
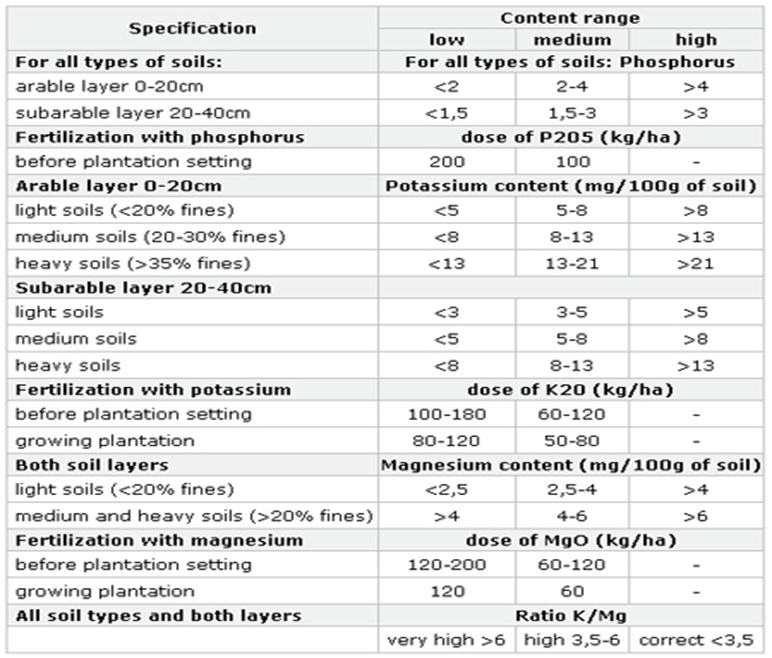
STRAWBERRY NUTRIENTS
Why Fertigation
The only method for possible for plastic mulched beds Increased yield and fruit quality Improved efficiency of application Flexibility to control plant growth response
Major Elements & Micro Nutrients
Nitrogen: |
Magnesium |
Phosphorus
|
BORON |
Potassium |
Maganese |
Calcium |
Iron |






